通常加排外锁就可以实现性能较好的队列,使用 Lock Free 实现,性能更高一点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync/atomic"
"unsafe"
)
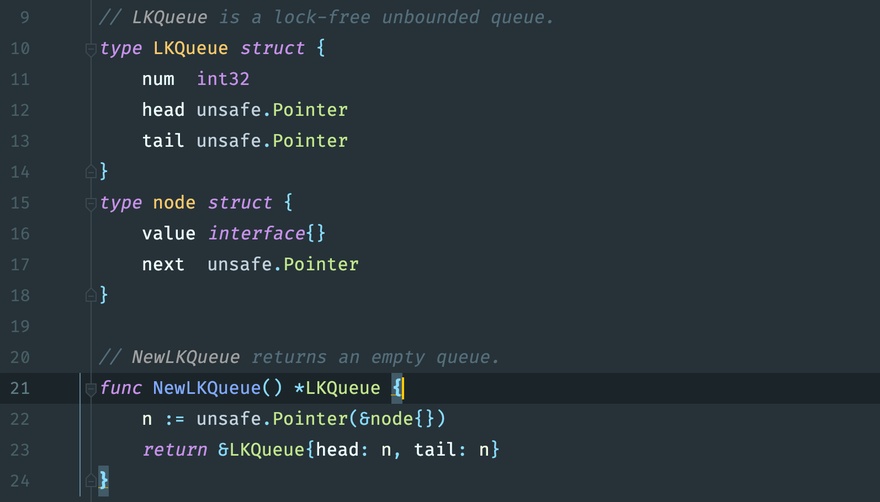
// LKQueue is a lock-free unbounded queue.
type LKQueue struct {
num int32
head unsafe.Pointer
tail unsafe.Pointer
}
type node struct {
value interface{}
next unsafe.Pointer
}
// NewLKQueue returns an empty queue.
func NewLKQueue() *LKQueue {
n := unsafe.Pointer(&node{})
return &LKQueue{head: n, tail: n}
}
// Enqueue puts the given value v at the tail of the queue.
func (q *LKQueue) Enqueue(v interface{}) {
n := &node{value: v}
for {
tail := load(&q.tail)
next := load(&tail.next)
if tail == load(&q.tail) { // are tail and next consistent?
if next == nil {
if cas(&tail.next, next, n) {
cas(&q.tail, tail, n) // Enqueue is done. try to swing tail to the inserted node
atomic.AddInt32(&q.num, 1)
return
}
} else { // tail was not pointing to the last node
// try to swing Tail to the next node
cas(&q.tail, tail, next)
}
}
}
}
// Dequeue removes and returns the value at the head of the queue.
// It returns nil if the queue is empty.
func (q *LKQueue) Dequeue() interface{} {
for {
head := load(&q.head)
tail := load(&q.tail)
next := load(&head.next)
if head == load(&q.head) { // are head, tail, and next consistent?
if head == tail { // is queue empty or tail falling behind?
if next == nil { // is queue empty?
return nil
}
// tail is falling behind. try to advance it
cas(&q.tail, tail, next)
} else {
// read value before CAS otherwise another dequeue might free the next node
v := next.value
if cas(&q.head, head, next) {
atomic.AddInt32(&q.num, -1)
return v // Dequeue is done. return
}
}
}
}
}
// Size return num of q
func (q *LKQueue) Size() int {
return *(*int)(unsafe.Pointer(q)) // q.num
}
func load(p *unsafe.Pointer) (n *node) {
return (*node)(atomic.LoadPointer(p))
}
func cas(p *unsafe.Pointer, old, new *node) (ok bool) {
return atomic.CompareAndSwapPointer(
p, unsafe.Pointer(old), unsafe.Pointer(new))
}
func main() {
q := NewLKQueue()
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
q.Enqueue(i)
fmt.Printf("Enqueue: %d, Size %d \n", i, q.Size())
}
for i := 0; i < 12; i++ {
fmt.Printf("Dequeue: %v, Size %d \n", q.Dequeue(), q.Size())
}
}
输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
Enqueue: 0, Size 1
Enqueue: 1, Size 2
Enqueue: 2, Size 3
Enqueue: 3, Size 4
Enqueue: 4, Size 5
Enqueue: 5, Size 6
Enqueue: 6, Size 7
Enqueue: 7, Size 8
Enqueue: 8, Size 9
Enqueue: 9, Size 10
Dequeue: 0, Size 9
Dequeue: 1, Size 8
Dequeue: 2, Size 7
Dequeue: 3, Size 6
Dequeue: 4, Size 5
Dequeue: 5, Size 4
Dequeue: 6, Size 3
Dequeue: 7, Size 2
Dequeue: 8, Size 1
Dequeue: 9, Size 0
Dequeue: <nil>, Size 0
Dequeue: <nil>, Size 0
本文网址: https://golangnote.com/topic/303.html 转摘请注明来源